合成数据生成#
[1]:
import json
from itertools import islice
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import AutoMinorLocator, MultipleLocator
[2]:
from gluonts.core import serde
from gluonts.dataset.artificial import recipe as rcp
[3]:
# plotting utils
def plot_recipe(recipe, length):
output_dict = rcp.evaluate(recipe, length)
K = len(output_dict)
lct = MultipleLocator(288)
minor = AutoMinorLocator(12)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(K, 1, figsize=(16, 2 * len(recipe)))
for i, k in enumerate(output_dict):
axs[i].xaxis.set_major_locator(lct)
axs[i].xaxis.set_minor_locator(minor)
axs[i].plot(output_dict[k])
axs[i].grid()
axs[i].set_ylabel(k)
def plot_examples(target, length, num, anomaly_indicator=None):
fix, axs = plt.subplots(num, 1, figsize=(16, num * 2))
for i in range(num):
xx = rcp.evaluate(
dict(target=target, anomaly_indicator=anomaly_indicator), length
)
axs[i].plot(xx["target"])
axs[i].set_ylim(0, 1.1 * np.max(xx["target"]))
axs[i].grid()
if anomaly_indicator is not None:
axs[i].fill_between(
np.arange(len(xx["target"])),
xx["anomaly_indicator"] * 1.1 * np.max(xx["target"]),
np.zeros(len(xx["target"])),
alpha=0.3,
color="red",
)
def print_dicts(*dicts):
for d in dicts:
print("{")
for k, v in d.items():
print("\t", k, ": ", v)
print("}\n")
数据生成 Recipe#
为了生成逼真的人工数据,我们通过符号图描述数据生成过程(这类似于 mxnet 符号图的工作方式)。
你的图可以包含 Python 值以及对应于随机变量或随机过程的运算符。一个 Recipe 的输出可以是一个列表、字典或一个值。
[4]:
rcp.evaluate(rcp.RandomGaussian(), length=5)
[4]:
array([-0.14623032, -1.06986359, 1.05844796, 0.75534637, -1.39678759])
[5]:
rcp.evaluate({"var1": rcp.RandomGaussian(), "var2": 3.0}, length=5)
[5]:
{'var1': array([ 1.4089298 , 1.38211622, 1.7198381 , -1.48442956, -0.63099337]),
'var2': 3.0}
[6]:
rcp.evaluate([3.0, rcp.RandomUniform()], length=5)
[6]:
[3.0, array([0.19885428, 0.60489994, 0.42505934, 0.2305186 , 0.24688702])]
[7]:
recipe = dict(myOutput1=rcp.RandomGaussian())
# multiple evaluations lead to different results, due to randomness
print_dicts(
rcp.evaluate(recipe, length=5),
rcp.evaluate(recipe, length=5),
)
{
myOutput1 : [ 0.45000225 -2.2213785 -0.1528156 1.42434522 0.3139183 ]
}
{
myOutput1 : [ 0.17910279 -0.31140746 -0.2432074 -0.15257331 1.40217193]
}
引用变量#
每次创建像 RandomGaussian 这样的随机变量时,该变量都指向一个新的独立随机变量。你可以重复使用和引用之前创建的随机变量。
[8]:
stddev1 = 2.0
stddev2 = rcp.RandomUniform(low=0, high=1, shape=(1,))
x1 = rcp.RandomGaussian(stddev=stddev1)
x2 = rcp.RandomGaussian(stddev=stddev2)
x3 = 2 * x2
recipe = dict(x1=x1, x2=x2, x3=x3)
# multiple evaluations lead to different results, due to randomness
print_dicts(rcp.evaluate(recipe, length=5), rcp.evaluate(recipe, length=5))
{
x1 : [-4.15236783 3.33089287 -1.7650173 4.31840226 -3.24158136]
x2 : [ 0.45371147 -1.22840268 -0.091649 0.56955048 0.31684371]
x3 : [ 0.90742294 -2.45680536 -0.183298 1.13910097 0.63368743]
}
{
x1 : [ 1.21217111 -1.03711262 0.44268618 -2.64438173 -0.20533495]
x2 : [ 0.13661998 -0.12320349 -1.00964885 -1.16800566 -0.95996586]
x3 : [ 0.27323996 -0.24640699 -2.01929769 -2.33601131 -1.91993172]
}
注意,你可以在上述示例中创建和使用中间随机变量,例如 stddev2,而无需将其包含在输出中。
[9]:
recipe = dict(random_out=rcp.RandomGaussian(shape=(1,)), fixed_out=np.random.randn(1))
# note that fixed_out stays the same;
# it's evaluated only once when the recipe is created
print_dicts(rcp.evaluate(recipe, length=1), rcp.evaluate(recipe, length=1))
{
random_out : [0.34182422]
fixed_out : [-0.8086896]
}
{
random_out : [-0.35283937]
fixed_out : [-0.8086896]
}
长度#
recipe 包中的大多数运算符都有一个 length 参数,该参数在表达式求值时自动传递。其思想是这些 recipe 用于生成固定长度的时间序列,并且大多数运算符生成的时间序列的各个组成部分具有相同的长度。
[10]:
recipe = dict(random_gaussian=rcp.RandomGaussian(), constant_vec=rcp.ConstantVec(42))
print_dicts(rcp.evaluate(recipe, length=3), rcp.evaluate(recipe, length=5))
{
random_gaussian : [ 0.15885871 -1.1668147 2.01667793]
constant_vec : [42. 42. 42.]
}
{
random_gaussian : [ 2.01354963 -2.28381719 0.14022704 -0.14361124 -0.95813227]
constant_vec : [42. 42. 42. 42. 42.]
}
运算符重载#
recipe 包中定义的运算符重载了基本的算术运算(加法、减法、乘法、除法)。
[11]:
x1 = 42 * rcp.ConstantVec(1)
x2 = x1 * rcp.RandomUniform()
x3 = rcp.RandomGaussian() + rcp.RandomUniform()
result = x1 + x2 + x3
rcp.evaluate(result, 3)
[11]:
array([60.47680942, 81.13694002, 70.76948986])
序列化/反序列化 (SerDe)#
由可序列化/可表示组件组成的 Recipe 可以轻松地进行序列化/反序列化。
[12]:
dumped = serde.encode(result)
print(dumped)
reconstructed = serde.decode(dumped)
rcp.evaluate(reconstructed, 3)
{'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe._LiftedBinaryOp', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'left': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe._LiftedBinaryOp', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'left': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe._LiftedBinaryOp', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'left': 42, 'op': '*', 'right': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe.ConstantVec', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'constant': 1}}}}, 'op': '+', 'right': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe._LiftedBinaryOp', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'left': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe._LiftedBinaryOp', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'left': 42, 'op': '*', 'right': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe.ConstantVec', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'constant': 1}}}}, 'op': '*', 'right': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe.RandomUniform', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'high': 1.0, 'low': 0.0, 'shape': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'builtins.tuple', 'args': [[0]]}}}}}}}, 'op': '+', 'right': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe._LiftedBinaryOp', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'left': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe.RandomGaussian', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'shape': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'builtins.tuple', 'args': [[0]]}, 'stddev': 1.0}}, 'op': '+', 'right': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'gluonts.dataset.artificial.recipe.RandomUniform', 'args': [], 'kwargs': {'high': 1.0, 'low': 0.0, 'shape': {'__kind__': <Kind.Instance: 'instance'>, 'class': 'builtins.tuple', 'args': [[0]]}}}}}}}
[12]:
array([83.17622164, 77.74813707, 77.95044445])
简单示例#
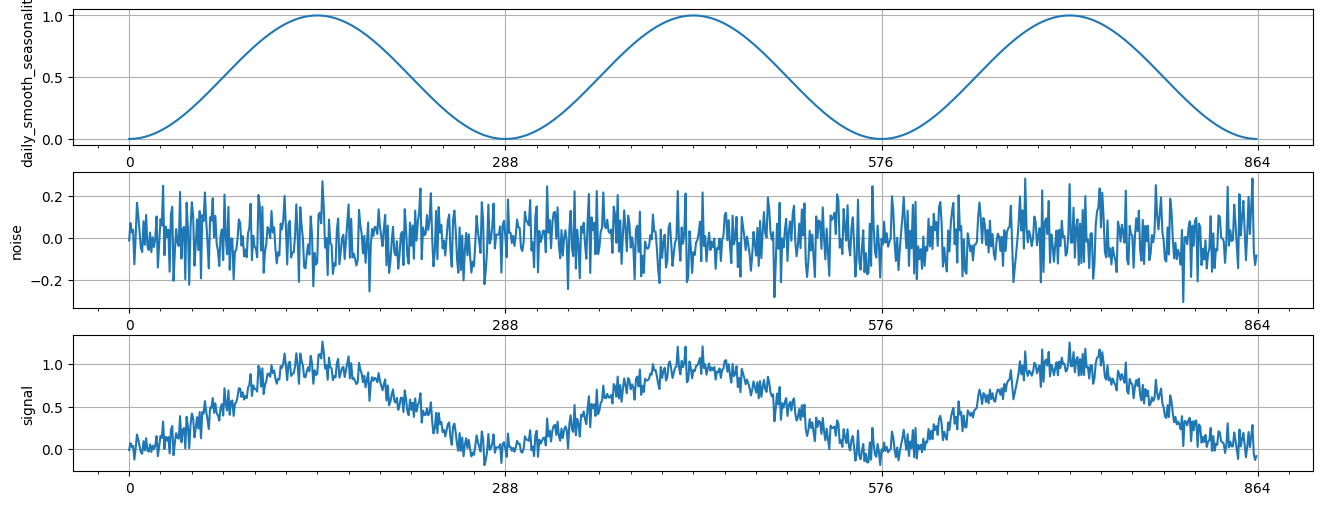
[13]:
daily_smooth_seasonality = rcp.SmoothSeasonality(period=288, phase=-72)
noise = rcp.RandomGaussian(stddev=0.1)
signal = daily_smooth_seasonality + noise
recipe = dict(
daily_smooth_seasonality=daily_smooth_seasonality, noise=noise, signal=signal
)
plot_recipe(recipe, 3 * 288)
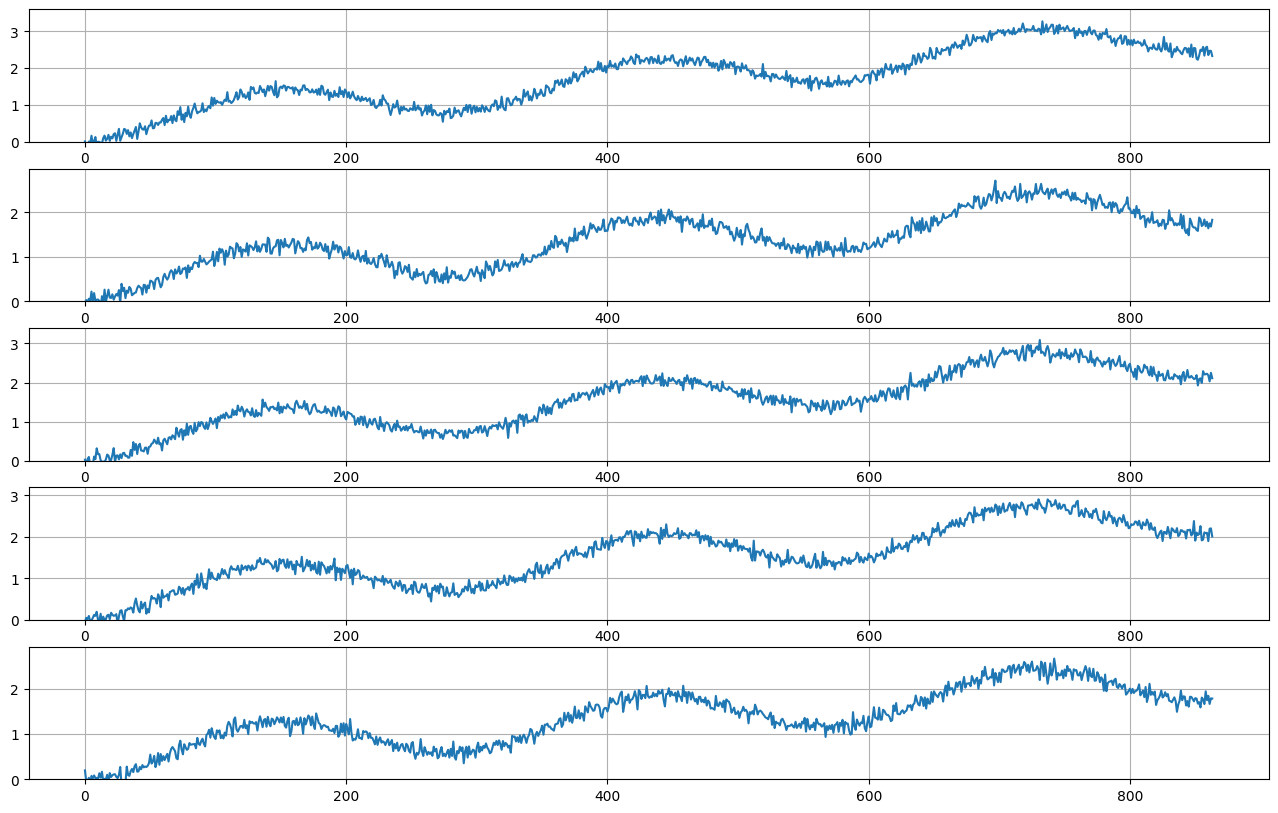
[14]:
slope = rcp.RandomUniform(low=0, high=3, shape=(1,))
trend = rcp.LinearTrend(slope=slope)
daily_smooth_seasonality = rcp.SmoothSeasonality(period=288, phase=-72)
noise = rcp.RandomGaussian(stddev=0.1)
signal = trend + daily_smooth_seasonality + noise
plot_examples(signal, 3 * 288, 5)
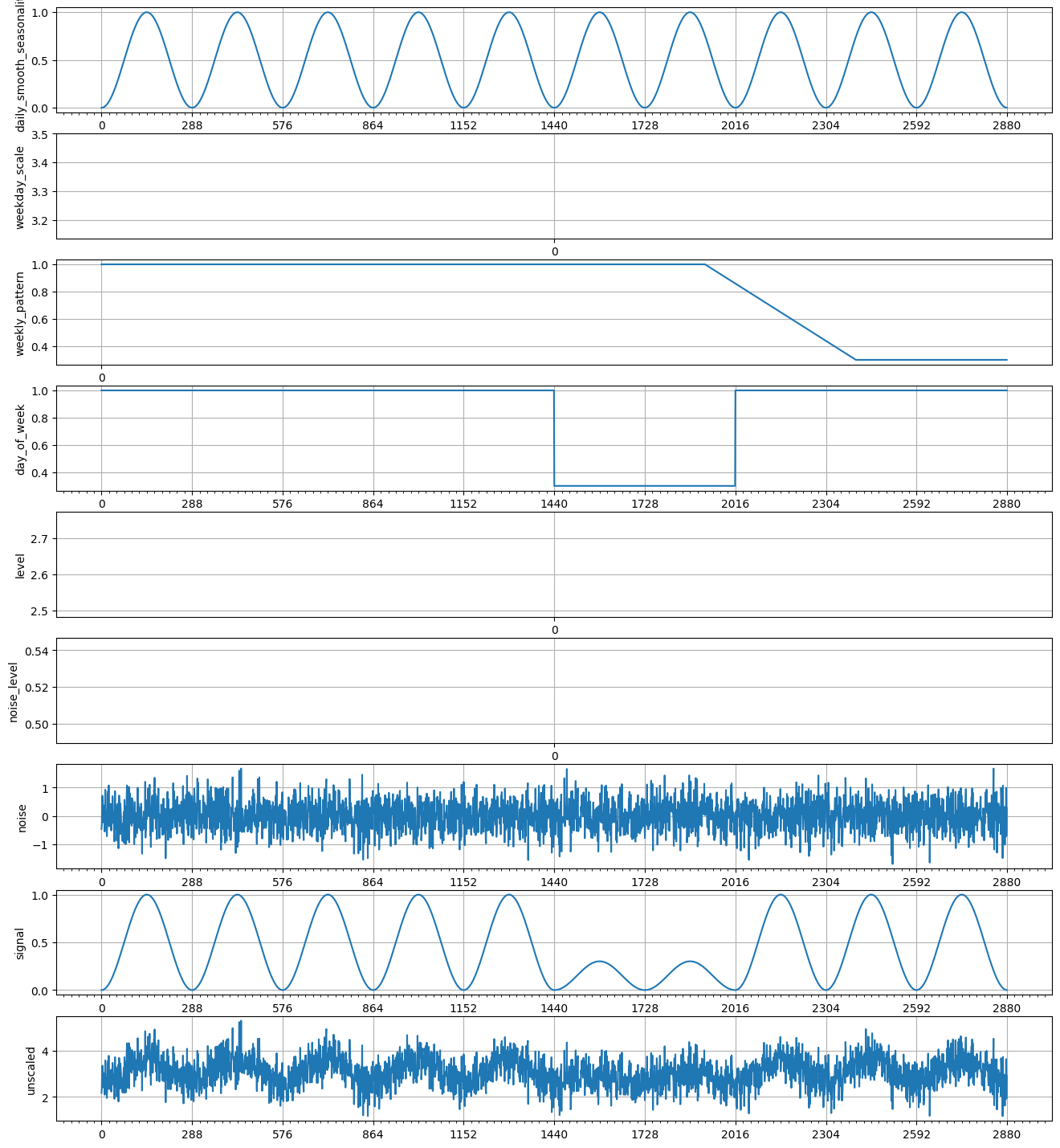
组合 Recipe#
有多种方法可以组合和扩展生成 Recipe。例如,使用 Python 函数。
[15]:
def weekly_seasonal_unscaled():
daily_smooth_seasonality = rcp.SmoothSeasonality(period=288, phase=-72)
weekday_scale = rcp.RandomUniform(0.1, 10, shape=(1,))
weekly_pattern = rcp.NormalizeMax(
rcp.Concatenate([weekday_scale * np.ones(5), np.ones(2)])
)
day_of_week = rcp.Dilated(rcp.Repeated(weekly_pattern), 288)
level = rcp.RandomUniform(low=0, high=10, shape=1)
noise_level = rcp.RandomUniform(low=0.01, high=1, shape=1)
noise = noise_level * rcp.RandomGaussian()
signal = daily_smooth_seasonality * day_of_week
unscaled = level + signal + noise
return dict(
daily_smooth_seasonality=daily_smooth_seasonality,
weekday_scale=weekday_scale,
weekly_pattern=weekly_pattern,
day_of_week=day_of_week,
level=level,
noise_level=noise_level,
noise=noise,
signal=signal,
unscaled=unscaled,
)
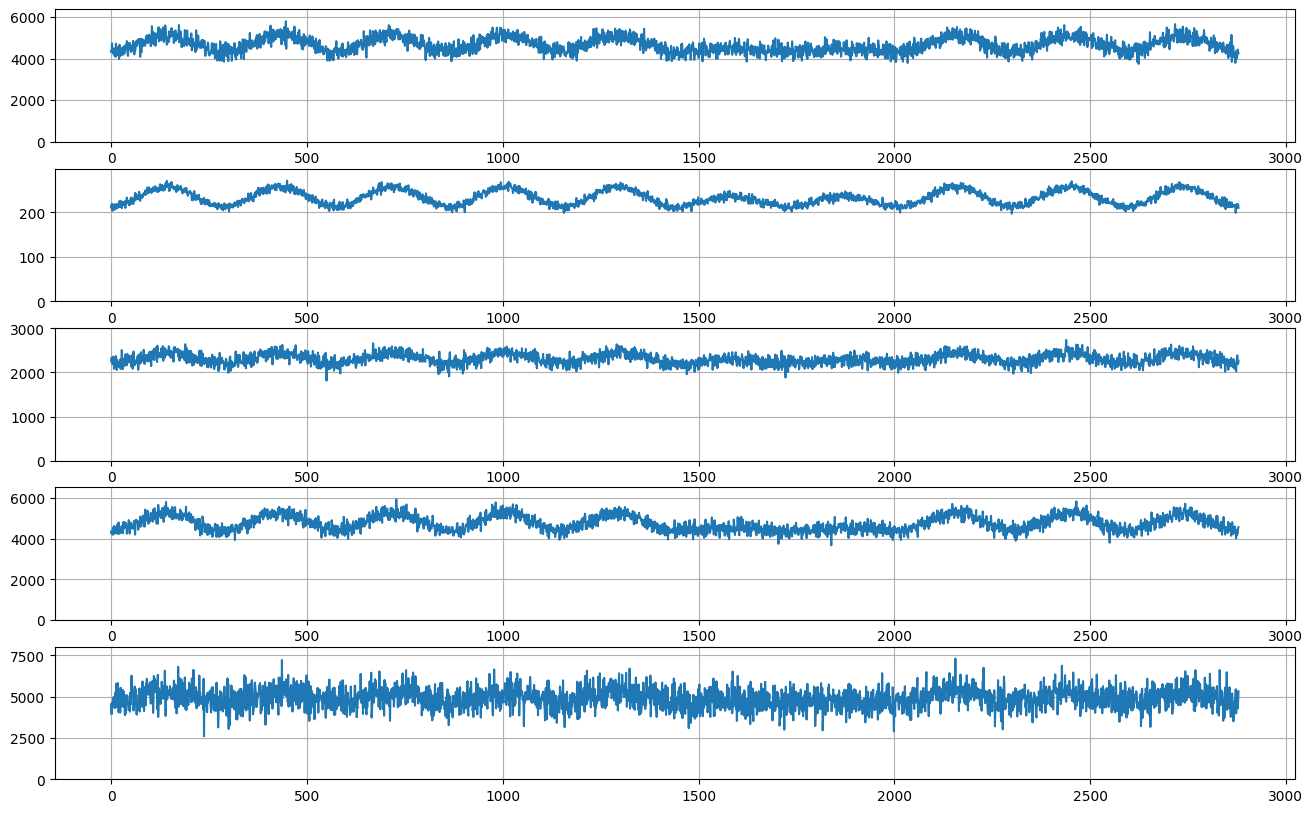
recipe = weekly_seasonal_unscaled()
plot_recipe(recipe, 10 * 288)
plot_examples(recipe["unscaled"], 10 * 288, 5)
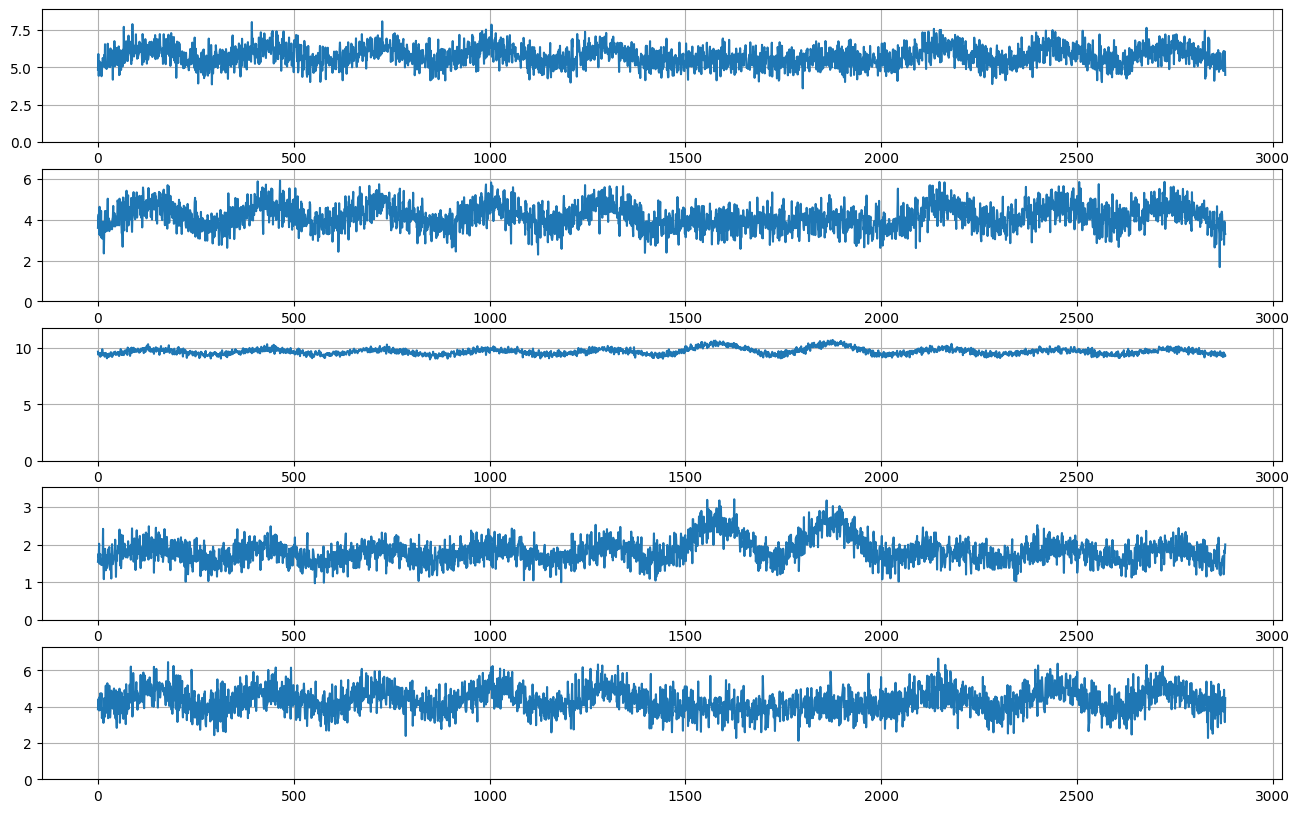
[16]:
def weekly_seasonal():
c = weekly_seasonal_unscaled()
unscaled = c["unscaled"]
scale = rcp.RandomUniform(low=0, high=1000, shape=1)
z = scale * unscaled
return z
plot_examples(weekly_seasonal(), 10 * 288, 5)
这里是一个更复杂的示例
[17]:
def scale(unscaled):
s = rcp.RandomUniform(low=0, high=1000, shape=1)
z = s * unscaled
return z
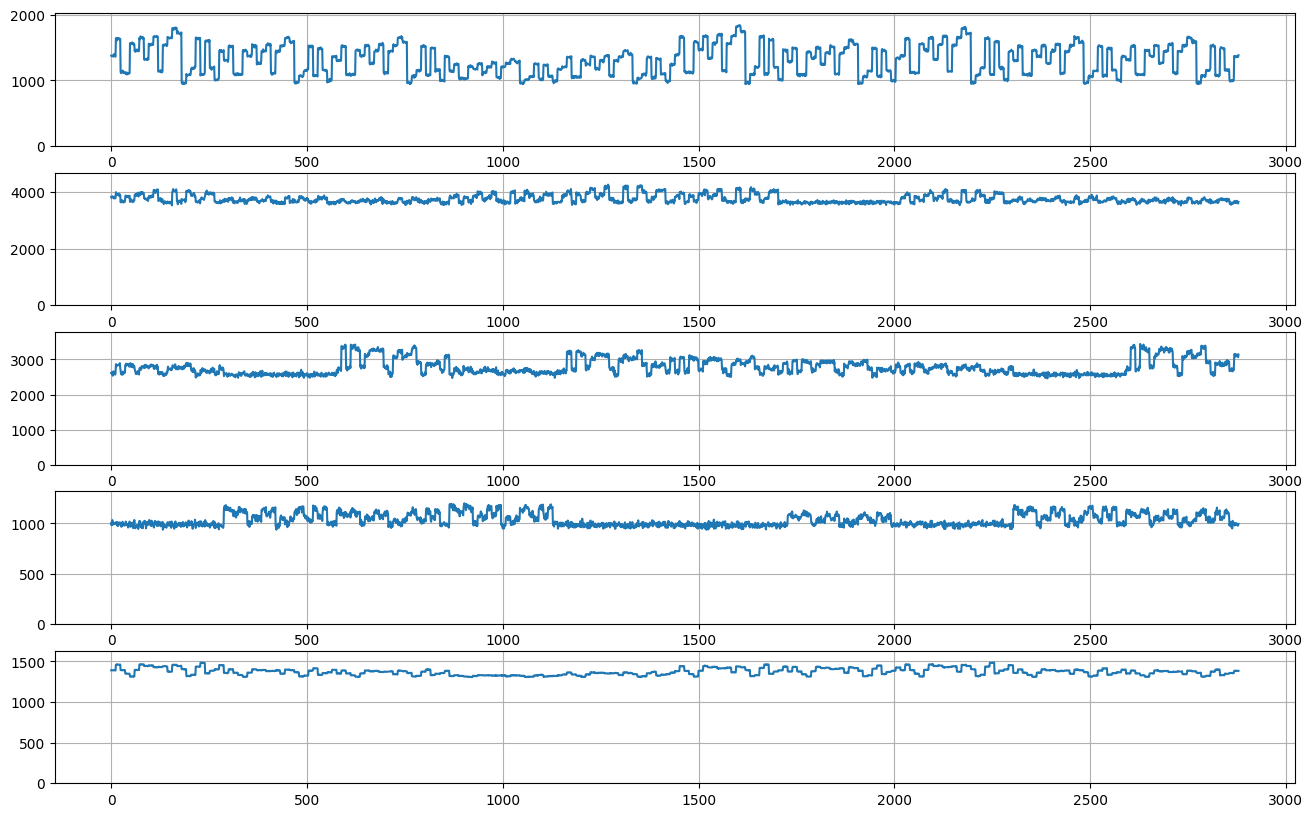
def complex_weekly_seasonality():
daily_pattern = rcp.RandomUniform(0, 1, shape=(24,))
daily_seasonality = rcp.Dilated(rcp.Repeated(daily_pattern), 12)
weekly_pattern = rcp.RandomUniform(0, 1, shape=(7,))
weekly_seasonality = rcp.Dilated(rcp.Repeated(weekly_pattern), 288)
unnormalized_seasonality = daily_seasonality * weekly_seasonality
seasonality = rcp.NormalizeMax(unnormalized_seasonality)
noise_level = rcp.RandomUniform(low=0.01, high=0.1, shape=1)
noise = noise_level * rcp.RandomGaussian()
level = rcp.RandomUniform(low=0, high=10, shape=1)
signal = level + seasonality
unscaled = signal + noise
return scale(unscaled)
plot_examples(complex_weekly_seasonality(), 10 * 288, 5)
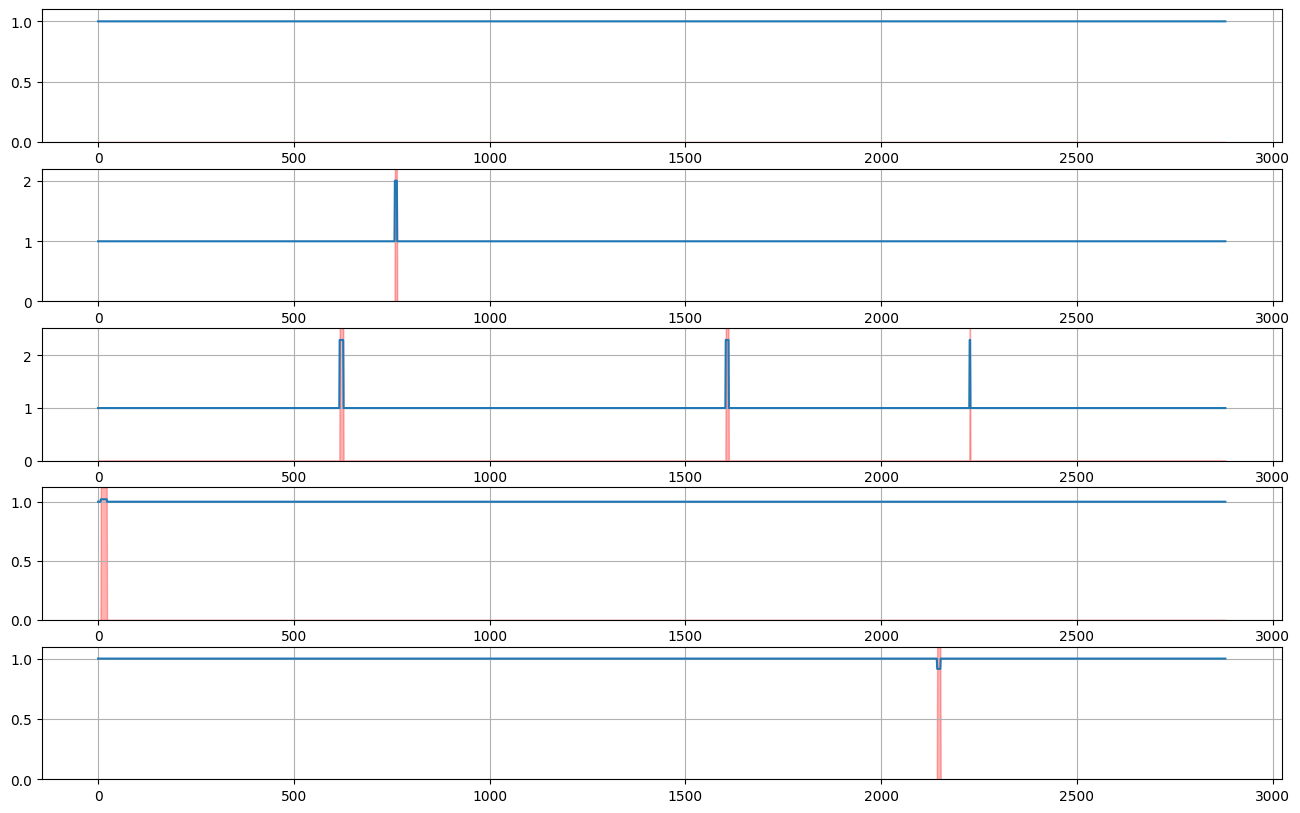
生成异常#
异常只是添加到基础时间序列或与基础时间序列相乘的另一种效应。我们可以定义一个用于创建特定类型异常的 Recipe,然后将其与一个基础 Recipe 组合。
[18]:
z = rcp.ConstantVec(1.0)
def inject_anomalies(z):
normal_indicator = rcp.BinaryMarkovChain(one_to_zero=1 / (288 * 7), zero_to_one=0.1)
anomaly_indicator = 1 - normal_indicator
anomaly_scale = 0.5 + rcp.RandomUniform(-1.0, 1.0, shape=1)
anomaly_multiplier = 1 + anomaly_scale * anomaly_indicator
target = z * anomaly_multiplier
return target, anomaly_indicator
target, anomaly_indicator = inject_anomalies(z)
plot_examples(target, 10 * 288, 5, anomaly_indicator)
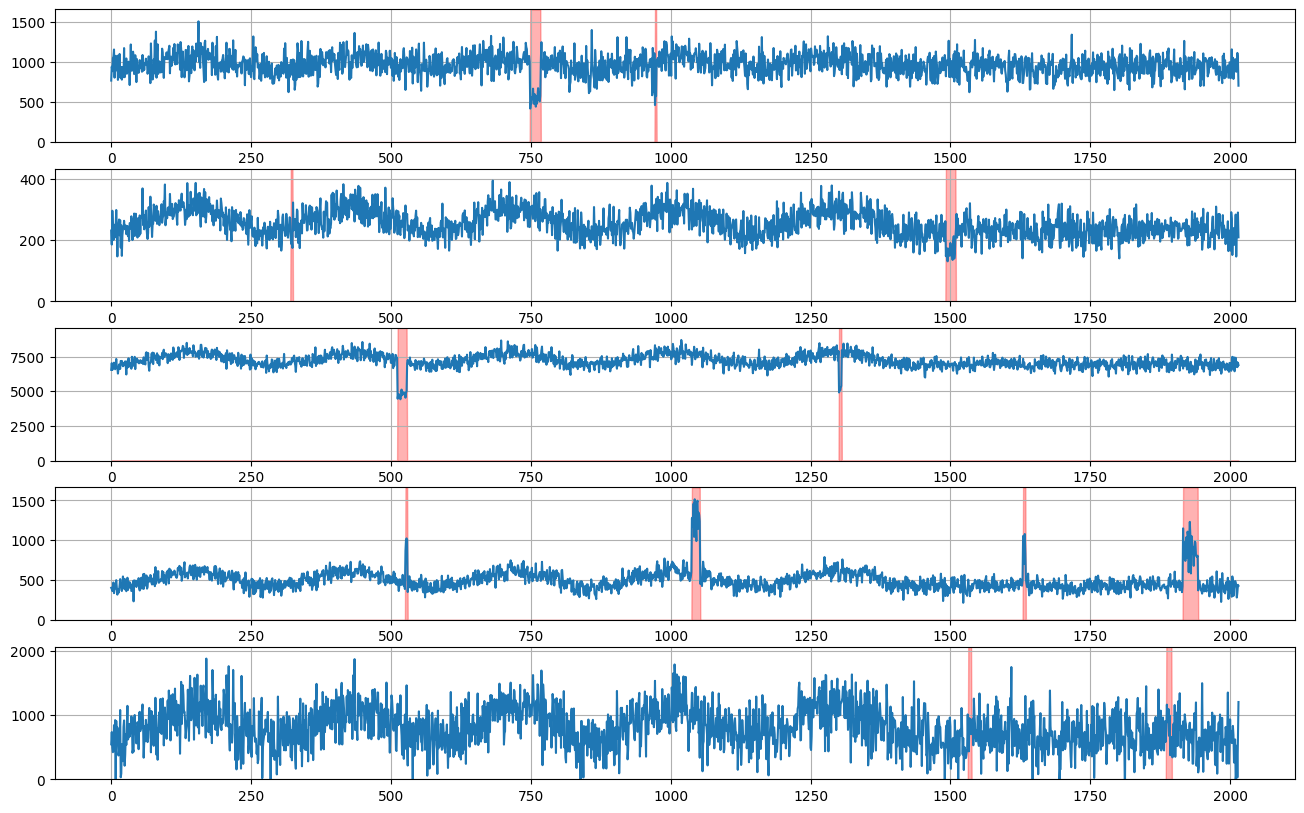
[19]:
target, anomaly_indicator = inject_anomalies(weekly_seasonal())
plot_examples(target, 288 * 7, 5, anomaly_indicator)
生成变化点#
[20]:
level = rcp.RandomUniform(0, 10, shape=1)
noise_level = rcp.RandomUniform(0.01, 1, shape=1)
noise = rcp.RandomGaussian(noise_level)
homoskedastic_gaussian_noise = level + noise
[21]:
z1 = homoskedastic_gaussian_noise
z2 = weekly_seasonal_unscaled()["unscaled"]
z_stacked = rcp.Stack([z1, z2])
change = rcp.RandomChangepoints(1)
unscaled = rcp.Choose(z_stacked, change)
target = scale(unscaled)
target, anomaly_indicator = inject_anomalies(target)
[22]:
plot_examples(target, 288 * 7, 10, anomaly_indicator)
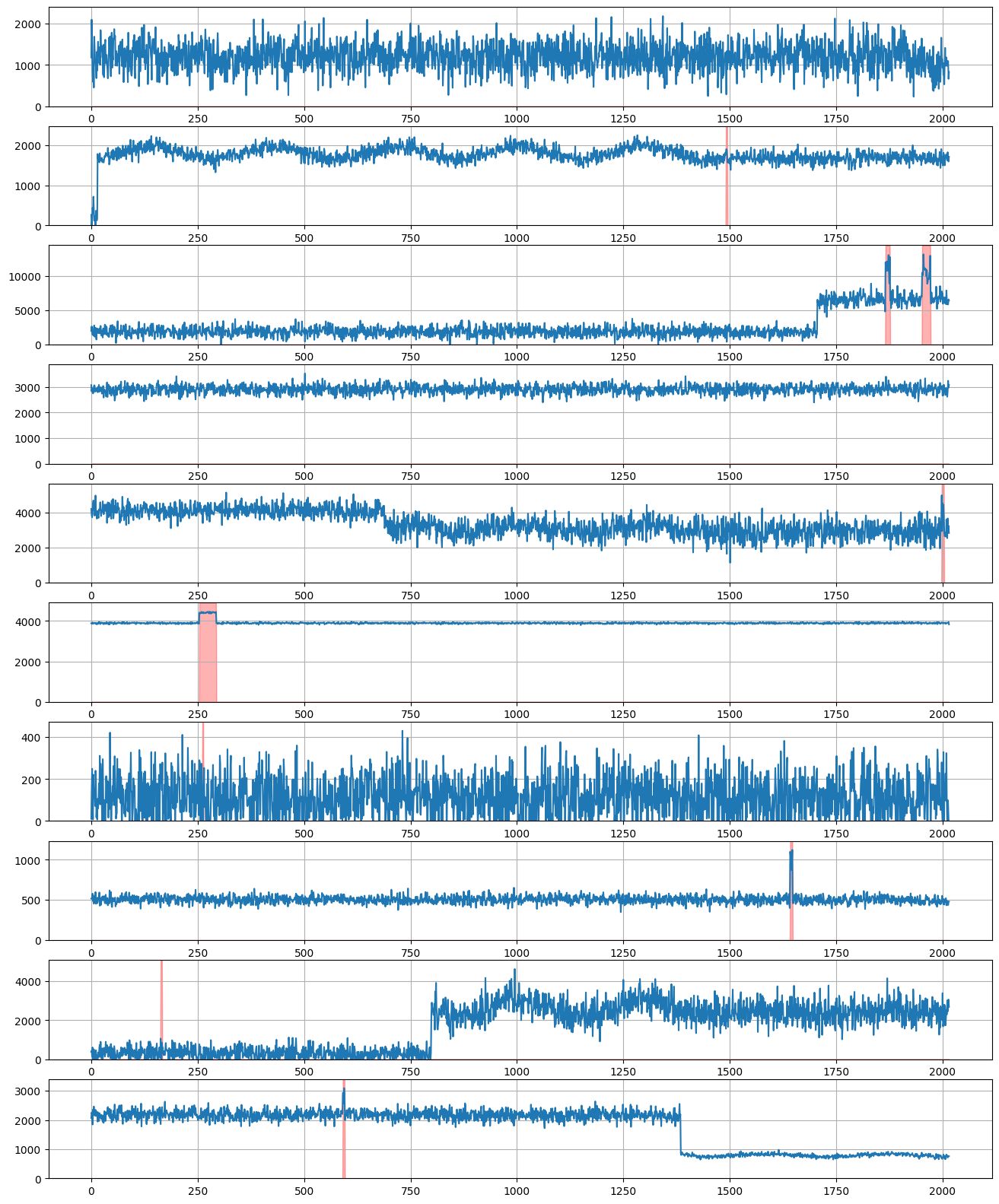
生成多个时间序列#
[23]:
rcp.take_as_list(rcp.generate(10, weekly_seasonal_unscaled(), "2018-01-01", {}), 2)
[23]:
[{'daily_smooth_seasonality': array([0. , 0.00011899, 0.00047589, 0.00107054, 0.00190265,
0.00297183, 0.00427757, 0.00581924, 0.00759612, 0.00960736]),
'weekday_scale': array([5.53325369]),
'weekly_pattern': array([1. , 1. , 1. , 1. , 1. ,
0.18072549, 0.18072549]),
'day_of_week': array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]),
'level': array([7.15189366]),
'noise_level': array([0.60673574]),
'noise': array([-1.37627579, 0.80910965, -0.5113108 , 1.19522357, 0.76819937,
-0.30693338, 1.54426428, 0.65576722, 0.29384949, 0.35138523]),
'signal': array([0. , 0.00011899, 0.00047589, 0.00107054, 0.00190265,
0.00297183, 0.00427757, 0.00581924, 0.00759612, 0.00960736]),
'unscaled': array([5.77561787, 7.9611223 , 6.64105875, 8.34818777, 7.92199568,
6.84793212, 8.70043552, 7.81348013, 7.45333928, 7.51288625]),
'item_id': '0',
'start': '2018-01-01'},
{'daily_smooth_seasonality': array([0. , 0.00011899, 0.00047589, 0.00107054, 0.00190265,
0.00297183, 0.00427757, 0.00581924, 0.00759612, 0.00960736]),
'weekday_scale': array([8.71312027]),
'weekly_pattern': array([1. , 1. , 1. , 1. , 1. ,
0.11476945, 0.11476945]),
'day_of_week': array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]),
'level': array([9.78618342]),
'noise_level': array([0.80116698]),
'noise': array([ 1.19700682, -0.16436603, 0.2508195 , -0.6842733 , -2.04537114,
0.52365764, 0.69255774, -0.59459811, 1.81845245, -1.16518975]),
'signal': array([0. , 0.00011899, 0.00047589, 0.00107054, 0.00190265,
0.00297183, 0.00427757, 0.00581924, 0.00759612, 0.00960736]),
'unscaled': array([10.98319024, 9.62193638, 10.03747882, 9.10298066, 7.74271494,
10.31281289, 10.48301873, 9.19740456, 11.612232 , 8.63060103]),
'item_id': '1',
'start': '2018-01-01'}]
保存到文件#
[24]:
def write_to_file(recipe, length, num_ts, fields, fn):
with open(fn, "w") as f, open(fn + "-all", "w") as g:
for x in islice(rcp.generate(length, recipe, "2019-01-07 00:00"), num_ts):
z = {}
for k in x:
if type(x[k]) == np.ndarray:
z[k] = x[k].tolist()
else:
z[k] = x[k]
xx = {}
for fi in fields:
xx[fi] = z[fi]
try:
f.write(json.dumps(xx))
except Exception as e:
print(xx)
print(z)
raise e
f.write("\n")
g.write(json.dumps(z))
g.write("\n")